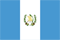
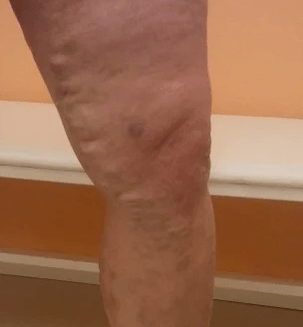
Varicose veins - This is the development of subcutaneous veins with a diameter of more than 3 mm.Varicose veins develop due to venous valve operation and venous wall weakness;At the same time, blood flow from the lower leg, increased pressure in the veins, which can cause chronic vein deficiency.
Occasionally, the television and reticular veins are mistaken for varicose-open.
This is a vein with diameter 3 mm and less, they do not affect the flow of veins, but cause a clear cosmetic defect.
What is the prevalence of varicose veins?
Development of subcutaneous vein varicose is present in 30 % of women and at 15 % of mature men.The prevalence of varicose veins from lower feet increases significantly with age and is present in most people over the age of 60.The proportion of patients with trophic disorders in adulthood is only 1.8%, while at the old age the indicator reaches 20%.At the same time, every fifth patient in life is faced with thrombophlebitis.Among the causes that lead to defects, the shape of the veins with disabilities is more than the artery.
The main risk factors for the development of varicose veins are:
- Old
- Female gender
- pregnancy
- Hormone disorders
- Positive family history
Additional risk factors:
- smoke
- Arterial hypertension
- constipation
Literature on additional risk factors.In addition, the risk of venous disease is low.
How is varicose veins shown?
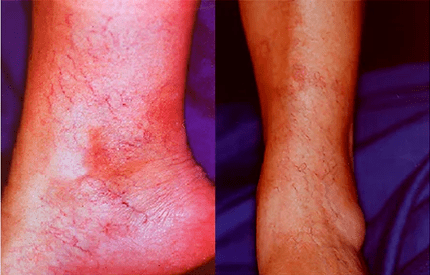
The most frequent manifestation is uneven expanded veins that stand out on the surface.In some cases, they are invisible or determined only by touch, on the other hand -they take the form of winding with the formation of nodes or appearance resembling a large bunch of grapes.
Usually varicose veins are accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Feelings and tension in the feet
- Pain attracts and/or pain along the veins
- Rapid fatigue fatigue
- Itching
Rare diseases can cause restless foot syndrome and night cramps.
What is the danger of the development of varicose veins?
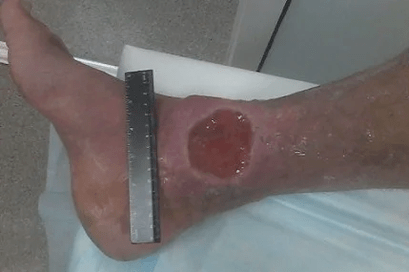
In the absence of treatment, the development of varicose veins can cause chronic vein deficiency (CVN).The presence of HVN shows severe violations of the return of lymph veins (clinical classes C3-C6 CEAP classification), including: chronic edema (lymphedem), skin color change (hyperpigmentation), venous eczema, skin compaction, trophic vein ulcer.
What is the complication of varicose veins?
Thromboflebitis-The formation of thrombus in the surface vein system is an event encountered with 20% of patients with varicose veins.Such thrombosis is accompanied by severe pain, redness of the skin, sealing along the veins in the lower leg and/or thighs.In the absence of treatment, thrombotic mass is possible to a deep vein system.
Inner vein thrombosis (TGV) - In most cases, the beginning of the process is without symptoms.When thrombosis spreads to the femoral segment and pelvic veins, the main blood flow from the lower leg is interrupted, accompanied by severe edema and pain syndrome and is considered a life -threatening condition.
Pulmonary artery thromboembolism (Tela) - In 10% of cases, thrombotic mass in deep veins in the lower leg is broken down and moved to the lung artery with blood flow, causing death.
What is needed for the correct diagnosis?
Given the various forms of vein, every detail of the history of the disease and the life of the patient, the presence of the same disease, the transaction, the outcome of the doctor's external examination and the most important thing is ultrasound, ultrasound, venous ultrasound scanning, it is important to make the right diagnosis.The latter, today, is the most accurate and informative method of studying the lower leg veins.
Treatment of varicose veins, the most common method:
- Treatment of drugs-vites has proven its effectiveness in reducing the symptoms of varicose veins, but they cannot eliminate varicose veins.Pharmacotherapy has been successfully used to prevent complications in risk groups, pre -operation and postoperative recovery.
- Compression treatment - Wear special medical knitwear in the form of golf, stock, tight.In some cases, multi -layer wraps with elastic bandage of various connections and hardware pneumo compression are used.The role of compression treatment is difficult to lower, it is present at almost every stage of chronic prevention and treatment.
- Introduction to the vein lumen that can cause its closure.This method is a standard of gold to eliminate reticular veins.It is successfully used in the treatment of non -diameter varicose veins and has restrictions on eliminating the pathological blood flow of the main subcutaneous vein.
- Classical operation - Combined phlebectomy, in modern performance is performed by patients under spinal or local anesthesia.In some cases, this is the only way that can be implemented when the target vein is very convincing and/or has a high connection.However, this method is lower than the endo vascular traumatic procedure.
- Venous Endo Laser Prison - Methods for treating varicose veins, where the veins are not removed, but are closed from the inside with laser radiation, which are carried directly into the wholesale vessel with fiber.The effectiveness of the procedure is comparable to the results of the vein surgery, at the same time, it is characterized by minimal trauma.Recovery time is 1-3 days.
- Radio frequency jail - a progressive way to eliminate the blood flow of the subcutaneous vein pathology.This is an outpatient procedure performed under local anesthesia.The effectiveness of the treatment corresponds to the classic phlebectomy level, the pain syndrome is minimal or absent.Recovery time is 1-2 days.